|
|
| |
|
 |
Thermal Plumes |
| |
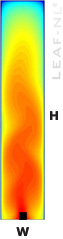 |
Thermal plumes or convection
from a localized heat source, where hot fluid penetrates into a colder
region above are encountered in nature and in many engineering
applications. Particular emphasis on the shape and time dynamics of
thermal plumes has been devoted indicating that it is a problem of
pattern formation. The fluid near the heat source receives heat
increasing its buoyancy, allowing the development of a primary fluid
pattern which evolves finally to a well known thermal plume. As the
plume rises losses its connection with the source which produced it.
The evolution of the cap of the plume at the first stages of its
formation reveals certain properties of its intrinsic nonlinear
character which are studied here through standard numerical methods and
from experiments. |
|
| The physical situation corresponds to a
small heat source of length b located at the bottom of a slender cavity
of aspect ratio H/W= 5. The heat source of size b (W=10b) has an
uniform and constant temperature Th while the side walls and the top
wall are kept at uniform temperature To. The rest of the bottom wall is
thermally insulated. Velocity vanishes on rigid walls. The set of
equations is the same in thermal plumes or Rayleigh Benard convection: |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|